Introduction to Hydraulic Power.
In general, power is defined as the relationship between the work done (force x distance) divided by the time it takes to complete that work.
In this article, we will explain how to calculate the power consumed by a specific hydraulic flow at a given working pressure. This way, we can verify whether the power of a motor is sufficient for the application or not.
Table of Contents
Calculation of Useful Hydraulic Power.
The power required by a hydraulic flow at a certain pressure is given by the following formula:
Useful Power (kW) = Flow Rate (liters/minute) x Pressure (bar) / 600
Thus, hydraulic power essentially depends on flow and pressure. Therefore, in two different hydraulic systems where the working pressure is the same, if the flow rate of the first system is double that of the second, the motor power driving the pump in the first system must also be twice as powerful as in the second system.
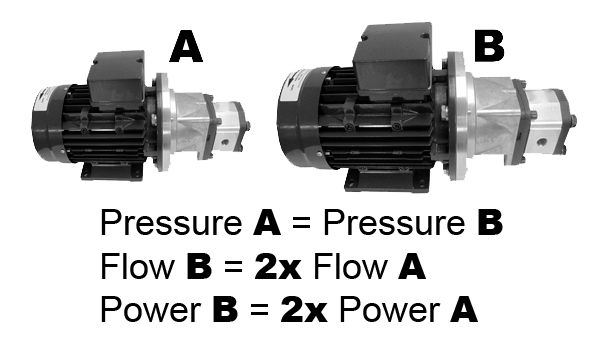
If flow rate A and flow rate B were equal but the working pressure of B were twice that of A, we would be in the same situation; the motor power would need to be double in B compared to A.
System Efficiency and Performance.
To calculate the power of the required motor (electric or combustion) for that useful power, two concepts need to be incorporated into the formula:
Efficiency of the hydraulic pump: we can assume a value of 90% (0.9). This value will depend on the type of pump (piston, gear, or vane pump) and its efficiency at a specific working pressure. Its value is obtained by multiplying the volumetric efficiency of the pump by its hydrodynamic efficiency.
For instance, in piston hydraulic pumps, the average total efficiency value is typically between 85% and 95%; in gear and vane pumps, efficiency usually ranges between 80% and 95%.
Mechanical efficiency of the transmission between the motor and the pump: we can also assume an approximate value of 90% (0.9).
Calculation of Required Hydraulic Power.
Therefore, the required motor power is given by the following formula:
Required Power = Useful Power / (0.9 x 0.9) = Useful Power / 0.81
Example of Hydraulic Power Calculation.
Pump flow rate = 30 liters/minute
Maximum pressure = 210 bar
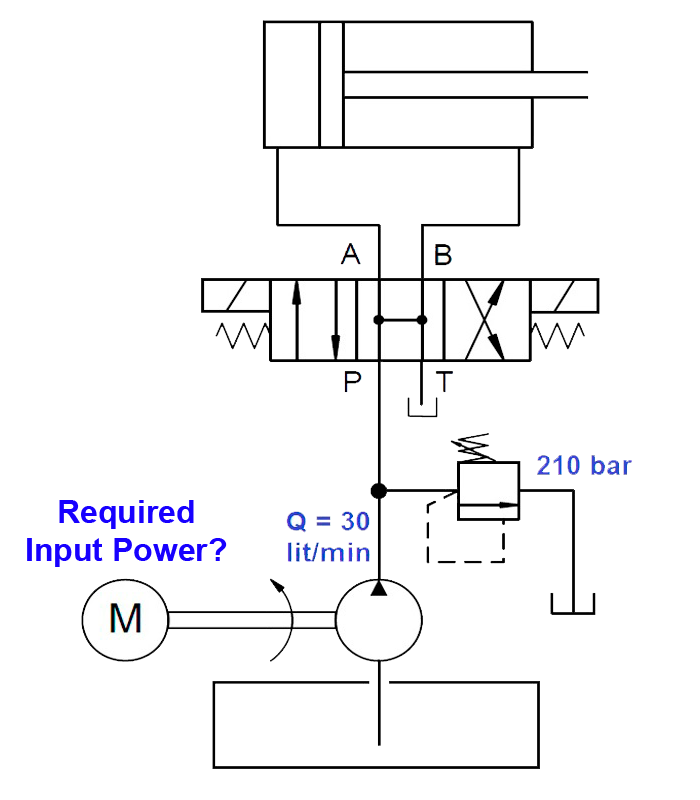
Useful Power (kW) = 30 liters/minute x 210 bar / 600 = 10.50 kW
Required Power (kW) = Useful Power (kW) / 0.81 = 10.50 / 0.81 = 12.96 kW
Once the required power is defined, a catalog motor with a power rating immediately above the calculated value should be selected.
For an electric motor, the model immediately above a power rating of 12.96 kW could be a 15 kW (20 HP) motor.
Units of Power.
In the International System of Units, the recognized unit for measuring power is the kW (kilowatt). In Britain, the HP (horsepower) is used, and in European countries and the United States, the CV (metric horsepower) is commonly used.
Equivalence Between Different Power Units.
Hydraulic Power Calculator.
Need help with your hydraulic calculations? Our experienced engineers can assist you in defining the required power as well as the dimensions of the hydraulic components needed for your application.
Create Date: 2024-11-03 15:40:00
Update date: 2024-11-03 15:40:00
SHIPPING WORLDWIDE
Let us assist you in choosing the perfect hydraulic component for your machine or upcoming project. We offer expedited shipping to anywhere in the world through top logistics companies such as DHL Express, TNT, FedEx or UPS.